Herein flexible bulk heterojunction bhj opds are fabricated on polyethylene terephthalate pet substrate by large scale roll to roll r2r micro gravure printing technique using the novel.
Roll to roll gravure printed electronics.
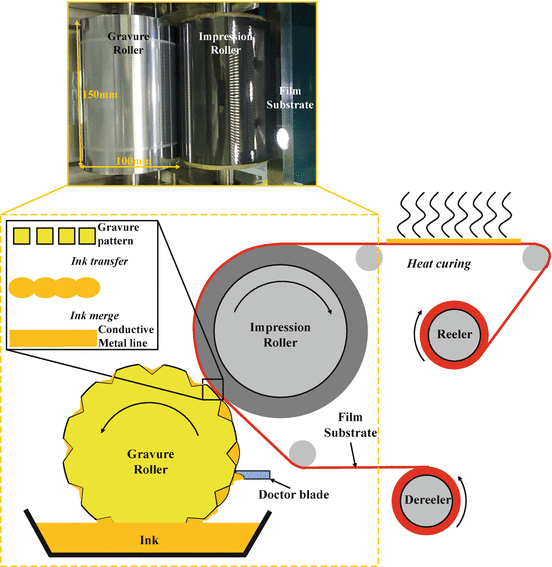
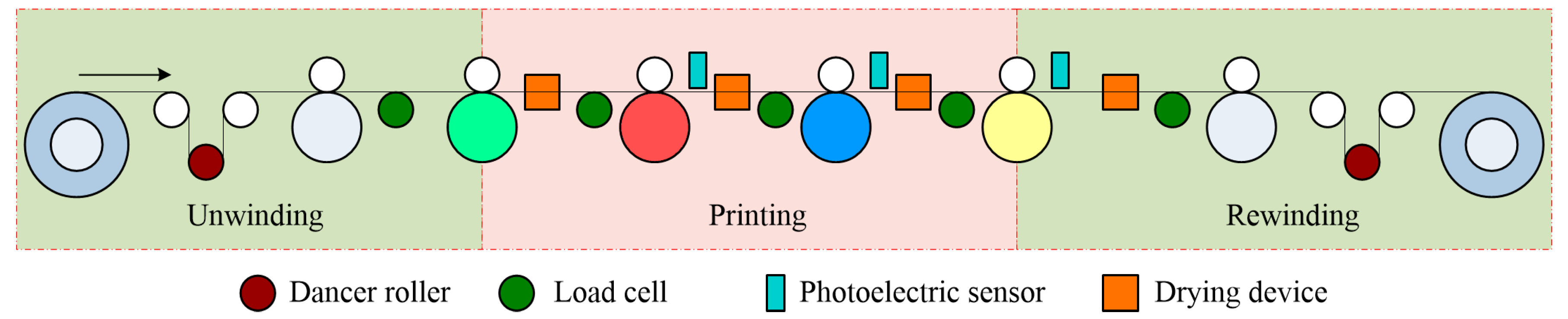
Large scale roll to roll r2r micro gravure printing process was developed to deposit the electron transport layer etl using low temperature solution processable zinc oxide zno nanoparticle ink on flexible substrate for fabricating inverted organic solar cells oscs.
Roll to roll r2r gravure printing is considered to be a leading technology for the production of flexible and low cost printed electronics in the near future.
In order to make laboratory scale research with this technique possible a custom table top gravure printing press was designed.
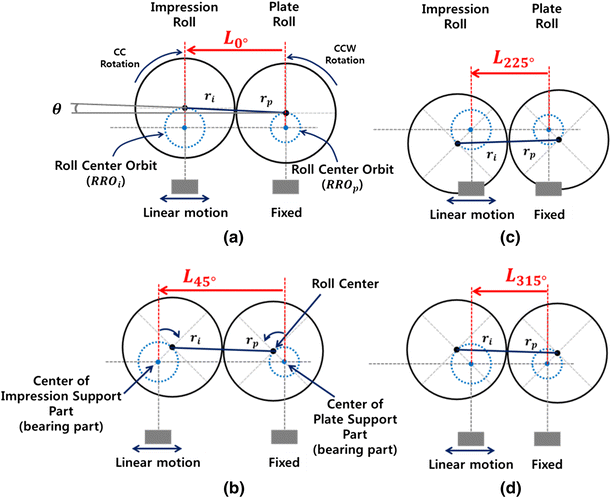
The widths and thicknesses of the printed electrodes were investigated with respect to the printing angle and printing speed.
To enable the use of r2r gravure in printed electronics the limits of overlay printing registration accuracy opra and the scalability of printed features with respect to the physical parameters of the gravure system including given plastic substrates and inks should be characterized.
Rolls with sub 5 μm resolution can be fabricated utilizing silicon microfabrication.
Toward this goal we present roll to roll r2r gravure printed electrodes that are robust under a range of electrochemical sensing applications.
Printed electronics is a set of printing methods used to create electrical devices on various substrates.
In this thesis gravure a printing process which offers the highest resolution highest speed and largest volume production in the graphic arts is demonstrated as a viable technique for printed electronics.
Roll to roll gravure printing is used to pattern source drain electrodes on plastic substrate while semiconductor and dielectric layers are printed by consecutive plate to roll gravure printing.
Physical understanding of the sub processes that constitute the gravure process namely filling wiping transfer and spreading is required to push the limits of gravure.
In addition the use of a low surface energy polyethylene terephthalate substrate was found to decrease the ink.
We use inks and electrode morphologies designed for electrochemical and mechanical stability achieving devices with uniform redox kinetics printed on 150 m flexible substrate rolls.
Tremendous progress has been made towards the use of gravure printing in highly scaled electronics.
This paper presents a novel method for printing thick silver electrodes with high fidelity using a rotogravure technique and high viscosity silver ink.
Printing typically uses common printing equipment suitable for defining patterns on material such as screen printing flexography gravure offset lithography and inkjet by electronic industry standards these are low cost processes.